
The Eternaut: Netflix Uses Generative AI for the First Time in an Original Production
Last Thursday, during the release of Netflix's second quarter 2025 results, Ted Sarandos, co-CEO of Netflix, confirmed the use of generative AI in The...
Generative AI, or GenAI, occupies a central place in the current artificial intelligence ecosystem, rapidly deploying across many sectors. In France, it is becoming a part of citizens' daily lives, particularly among young people, where its penetration reaches 76% among 18-34 year-olds, as revealed by a recent study by Havas Market. This phenomenon is accompanied by increased use in various fields such as health, leisure, and travel, demonstrating its potential to provide personalized and contextual responses. In the educational field, the Ministry of National Education has developed a framework to guide the use of GenAI in schools, emphasizing its role as an assistant rather than a substitute in the learning process. Students are now trained from primary school, with use allowed under supervision from the fourth grade, reflecting a willingness to prepare future generations for these new technologies.
Meanwhile, French companies show notable optimism regarding the adoption of generative AI, seen as a major productivity lever. A study by Cognizant, in collaboration with Oxford Economics, highlights a favorable environment in France, where 40% of leaders consider the regulatory framework conducive. However, challenges remain, notably the skills shortage, pushing companies to launch internal training programs. Despite these obstacles, the potential of GenAI as an innovation engine is recognized, with varied applications across sectors, illustrating diversified sectoral adoption. In the aeronautics field, Europrop International has opted for LightOn's Paradigm solution, thus integrating generative AI into its operations to optimize knowledge management while preserving the confidentiality of strategic data.
The adoption dynamics of generative AI are accompanied by significant technological developments. Baidu, a major Chinese player, has launched ERNIE 4.5 and ERNIE X1, two open-source models offering advanced multimodal understanding and reasoning performance at competitive costs. Their integration into tools like Ernie Bot aims to democratize access to these technologies while boosting competitiveness against American models. Furthermore, Google has made its NotebookLM tool available in a multilingual version, thus expanding its accessibility and content synthesis and management capabilities, particularly useful in the educational sector. These technological advances enhance the attractiveness of generative AI, while raising the question of governance and data management, which remains a major challenge for companies seeking to fully exploit these technologies.
Finally, the Spinoza project, led by Reporters Without Borders and the Alliance of General Information Press, underscores the importance of developing ethical generative AI tools dedicated to journalism. This initiative aims to enrich the work of journalists with reliable data while respecting the intellectual property of media. The "SpinozIA" report presents a series of recommendations to frame the use of AI in newsrooms, thus ensuring the integrity of information in AI systems used in journalism. This project demonstrates the desire to reinvent journalism in the digital age by integrating AI responsibly and ethically, while reaffirming the central role of newsrooms in producing quality content. These efforts highlight the ethical and strategic issues of generative AI, calling for continuous reflection on its integration into our societies.
Generative AI is a subcategory of artificial intelligence that uses algorithms to create new data similar to that on which it was trained. It primarily operates through large language models (LLM) and deep neural networks, enabling the generation of text, images, music, and much more.
Since its inception, generative AI has evolved from simple text generation models to systems capable of creating complex visual and audio content. This technology has seen a major acceleration with the introduction of models like OpenAI's GPT and DALL-E, increasing its precision and applicability.
Generative AI finds applications in many sectors: education, where it helps personalize learning; commerce, where it optimizes shopping experiences; and media, where it enriches content creation. It is also used for image recognition and artistic creation.
Key players in generative AI include companies like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft. In France, startups like Mistral AI and LightOn play a key role, supported by initiatives like the SpinozIA project for ethical journalism.
Despite its advances, generative AI faces challenges such as managing hallucinations, data protection, and environmental impact. Researchers are working on solutions to improve the reliability and energy efficiency of models.
Training in generative AI requires an understanding of machine learning and deep learning concepts. Courses are available online through platforms like Coursera and Udacity, as well as specialized university programs.
The future of generative AI is promising with innovations expected in the integration of autonomous agents and the improvement of LLMs. Companies continue to invest heavily, anticipating significant gains in productivity and innovation.
Generative AI transforms businesses by optimizing creation processes and enhancing service personalization. It offers growth opportunities in various sectors, from healthcare to finance, to marketing.
Generative AI uses advanced algorithms to create new data similar to that on which it was trained. It primarily operates through large language models (LLM) and deep neural networks. These models are capable of generating text, images, and even music by learning from vast datasets. Generative AI relies on techniques like supervised and unsupervised learning to refine its creative and analytical capabilities.
Generative AI is used in various fields, notably education, where it personalizes students' learning paths, and commerce, where it optimizes the customer experience and shopping journey. In media, it enriches content creation by generating articles, images, and videos. Other applications include product design, music and art generation, and voice synthesis for virtual assistants.
Generative AI has significantly evolved with the introduction of advanced language models like GPT and DALL-E. These innovations have improved the accuracy and diversity of generated content. Advances in computing power and data availability have also played a crucial role in this evolution. Current models are more performant, capable of generating multimodal content and adapting to various contexts.
The main players in generative AI include tech companies such as OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, which develop cutting-edge language models. In France, startups like Mistral AI and LightOn are emerging with innovative solutions. Initiatives like the SpinozIA project, supported by Reporters Without Borders, aim to integrate generative AI into specific fields like journalism, ensuring ethical practices.
Future trends in generative AI include the development of autonomous agents capable of making complex decisions, improving the energy efficiency of models, and integrating AI into new sectors like healthcare and agriculture. Prospects also include increased collaboration between companies to create personalized solutions and increased investment in research and development to overcome current challenges.
To train in generative AI, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles of machine learning and deep learning. Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and edX offer online courses on these topics. Universities also offer specialized programs in artificial intelligence. It is recommended to get acquainted with tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch, which are widely used in the development of generative models.
Generative AI faces several technical challenges, including managing hallucinations, where models generate incorrect or incoherent information. Data protection and privacy are also major concerns, as is the environmental impact related to the energy consumption of models. Researchers are working on solutions to improve the reliability, efficiency, and transparency of generative AI systems.
Generative AI transforms businesses by optimizing creation processes and enhancing service personalization. It allows for cost reduction, accelerates product development, and improves customer experience. In sectors like marketing, education, and healthcare, generative AI offers opportunities for growth and innovation by automating complex tasks and providing data-driven insights.
8 articles liés à ce sujet

Last Thursday, during the release of Netflix's second quarter 2025 results, Ted Sarandos, co-CEO of Netflix, confirmed the use of generative AI in The...

In response to the increasing use of AI in education, the Ministry of National Education has opted to regulate this practice, emphasizing respect for...

Generative AI is increasingly adopted by the French, especially among 18-34 year-olds with 76% of users, according to a study by Havas Market. AI infl...

Google announces that NotebookLM, its intelligent note-taking tool based on generative AI, is now available in a multilingual version. Initially offer...

Despite tangible results, French companies struggle to scale generative AI use. Snowflake's report highlights measurable ROI but modest budget commitm...
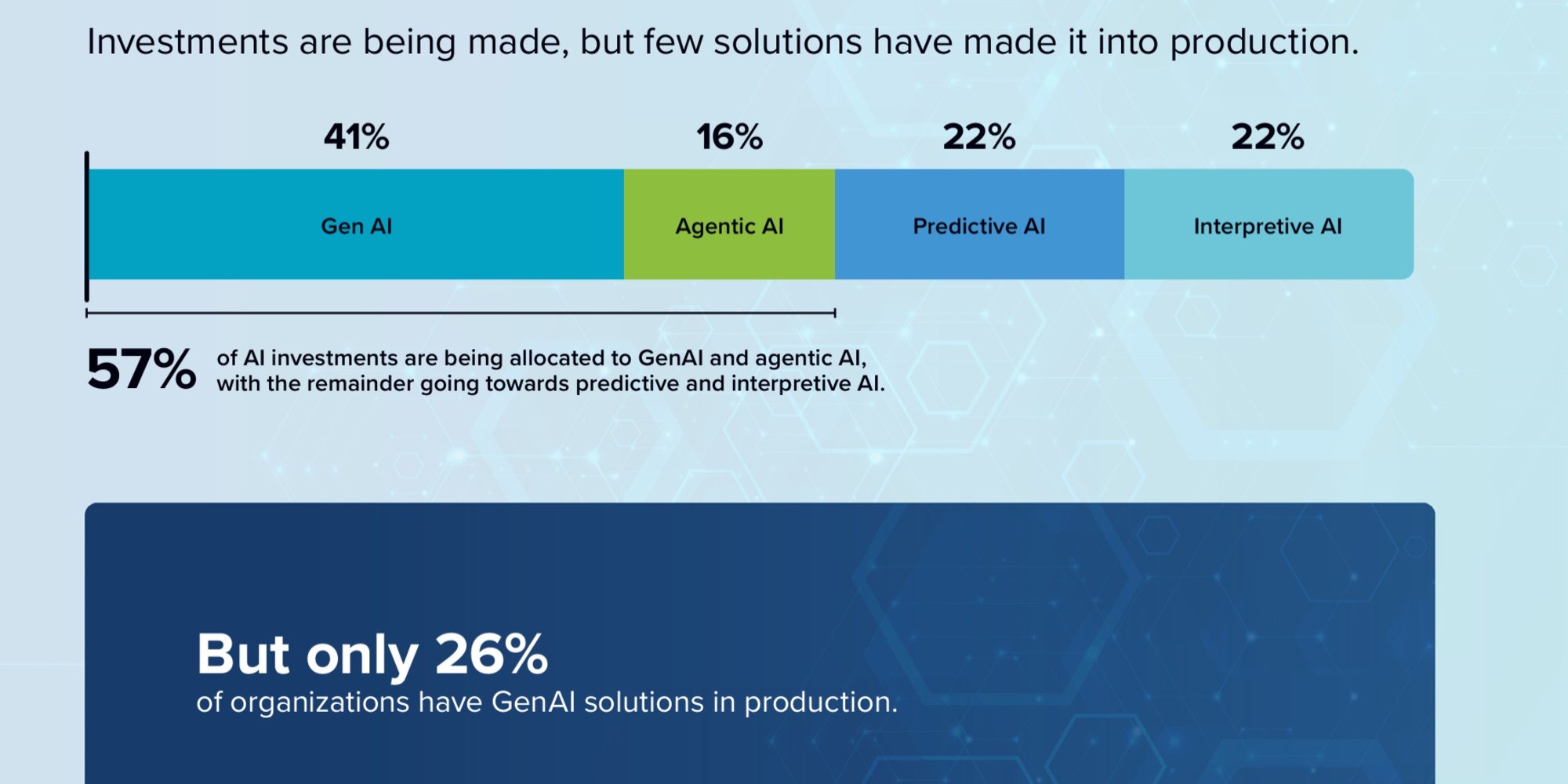
According to Qlik, bridging the gap between ambition and reality becomes urgent for businesses as they face challenges in effectively adopting GenAI.

With the launch of R1, DeepSeek not only created a shockwave in Silicon Valley but also intensified competition within the Middle Kingdom.

The NVIDIA GTC conference, a major annual event for artificial intelligence and accelerated computing professionals, will take place from March 17 to...