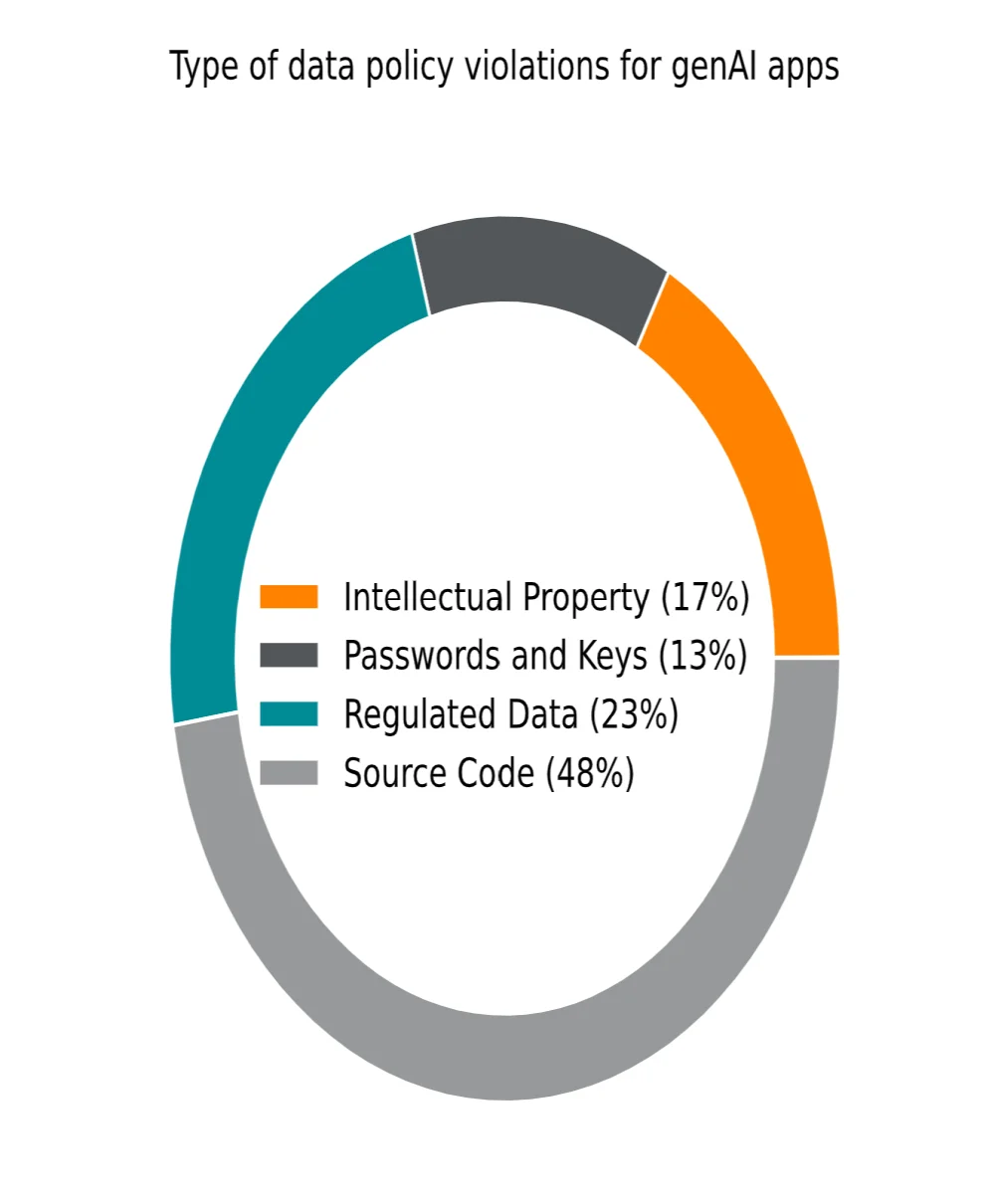
The increasing adoption of GenAI is redefining the technological landscape of enterprises, offering significant productivity gains while amplifying cybersecurity and data management risks. According to the 2025 Generative AI Cloud and Threat Report by Netskope, a leader in security and networking, the volume of data shared with generative AI applications has increased 30-fold in a year, including sensitive elements such as source code, regulated data, passwords, or encryption keys. This transformation requires organizations to reassess their security strategies to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of their critical information. In 2023, generative AI was still an emerging technology, dominated by ChatGPT and Google's Gemini. Only 1 in 100 enterprise users accessed these tools. By 2025, this proportion has significantly increased: almost 1 in 20 users directly exploits GenAI applications, while the majority benefit indirectly from their integration into various professional solutions.
Netskope identified 317 distinct GenAI applications used by over 3,500 of its clients, confirming the widespread adoption of these tools in modern workflows.
Ray Canzanese,
Netskope Threat Labs Director, highlights:
"The latest data shows that generative AI is no longer a niche technology, but is ubiquitous. It is increasingly integrated into all areas, whether through dedicated applications or back-end integrations. Such ubiquity presents a growing challenge for cybersecurity." Increased Risks to Data Security
This massive adoption comes with significant risks. Companies see their confidential data potentially exposed to third-party applications that could exploit them to train new AI models. Furthermore, generative AI fuels shadow IT: 72% of enterprise GenAI users access these tools from unsecured personal accounts, thus escaping IT department control.
Meanwhile, the rise of on-premises AI infrastructures, which increased from less than 1% to 54% in a year, mitigates some cloud-related risks but introduces new challenges, including internal data leaks within supply chains and vulnerabilities.
James Robinson, CISO of
Netskope, comments:
"Despite the serious efforts made by companies to implement internally managed generative AI tools, our study shows that shadow IT has been replaced by a ghost AI, with nearly three-quarters of users still accessing generative AI applications from their personal accounts. This ongoing trend, along with the data being shared, underscores the need to implement advanced data security measures to allow security and risk management teams to regain governance and visibility, both indispensable elements, as well as an acceptable control over how generative AI is used within their company."
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Faced with these threats, nearly 100% of companies are striving to reduce risks related to AI. Among the measures adopted,
Netskope reports:
Blocking and restricting access: many organizations prefer to prohibit access to GenAI applications until a thorough assessment is conducted;
Data loss prevention (DLP): monitoring and filtering solutions are implemented to prevent the inadvertent sharing of sensitive data with AI tools;
Real-time user coaching: training and contextual alerts help raise employee awareness of risks and guide them towards better usage practices.
Netskope's Recommendations
As cybercriminals exploit generative AI to develop increasingly sophisticated threats, companies must also evolve. As emphasized by Ari Giguere, Vice President of
Netskope, effective
cybersecurity must combine human creativity and technological power to keep up with the pace of innovation. Adopting specific frameworks and advanced security systems not only reduces risks but also leverages the numerous advantages offered by generative AI.
To protect data, users, and networks,
Netskope advocates implementing a structured approach:
Evaluate the generative AI landscape: Identify the GenAI applications and infrastructures used, along with their users and uses;
Strengthen control over GenAI applications: Only authorize validated applications, block unapproved ones, and use data loss prevention (DLP) technologies to prevent any leaks of sensitive information;
Optimize local controls : Apply reference frameworks such as the OWASP
LLM Top 10, NIST's AI risk management framework, and the MITRE
Atlas framework to ensure effective protection of internal infrastructures.
:
To better understand
What is 'shadow IT' and how does it impact the security of companies using GenAI?
Shadow IT refers to the use of IT systems, software, or applications without official approval from IT departments. It poses a security risk as it bypasses established control and security protocols, increasing vulnerability to data breaches, especially with the growing use of GenAI.
How has the evolution of AI infrastructure, from cloud to on-premises, impacted corporate cybersecurity strategies?
The shift to on-premises AI infrastructure has allowed companies to better control their data, thus reducing some cloud-associated risks like data breaches. However, it has also introduced new challenges, such as securing internal supply chains and managing local vulnerabilities, prompting companies to adapt their cybersecurity strategies.